CCTV
system consists of many components and each is critical to the quality
of the video picture that is reproduced. Many system designers specify
very specific criteria for the hardware; however, when it comes to the
transmission media, only general information is given.
Selecting
the correct transmission media for CCTV is one of the most vital
aspects of designing a quality system and yet it is the least
understood topic in system design. You can have the highest quality
hardware components in a system but if the video signal is not
transmitted by the proper media, your whole system will suffer. Many
of the common video problems with picture quality can be avoided by
selecting the proper transmission media and following proper
installation techniques and procedures.
|
CCTV Selection Guide
|
|
RG59
|
| RG59B |
RG59
CMG/FT4 |
| RGP59A |
RG59
Plenum CMP/FT6 |
| RG59E |
RG59
Stranded CMH/FT1 |
|
RG6
|
| RG6D |
RG6
Burial |
| RGP6F |
RG6
Plenum CMP/FT6 |
| RG6K |
RG6
Stranded CMG/FT4 |
| RG6N |
RG6
CMR/FT4 |
|
RG11 |
| RG11D |
RG11
CMH/FT1 |
| RGP11E |
RG11
Plenum CMP/FT6 |
Coaxial
Cable Types
CCTV
video signals are commonly transmitted using coaxial cable. Coaxial
cable is designed to transmit the complete video frequency range with
minimum distortion or attenuation, making it an excellent choice for
CCTV. However, choosing the incorrect coaxial cable can degrade the
overall signal transmission and/or allow outside EMI/RFI interference
to be introduced into the signal causing high noise levels. This in
turn can result in poor picture quality.
There
are various construction types for coaxial cable. Understanding the
various parameters of coaxial cable and selecting the proper cable for
a CCTV system will eliminate wasted time, money, and aggravation. A
CCTV video signal is comprised of both low frequency components
(horizontal and vertical sync pulse information), and high frequency
components (video information). In order to transmit this full
spectrum of frequencies with little distortion or attenuation, it is
important to select the correct cable that meets the specifications
for CCTV transmission.
The
parameters to consider are mechanical characteristics such as the
center conductor material, dielectric material, shield type and
material, and jacket material. The electrical characteristics such as
resistance, capacitance, impedance and attenuation are critical for
proper transmission. The following explains each component:
Center
Conductor
Center
Conductor material made of bare cooper is recommended for optimum
performance in CCTV signal transmission. Because a CCTV video signal
is a baseband composite video with fairly low frequency components
compared to a CATV video signal, the low D.C. resistance that copper
provides will greatly improve the video signal transmission. if the
cable is going to be used on a CCTV camera that will be in a fixed
position, then a solid conductor is acceptable. However, if the cable
will be used in a pan and tilt application, then you should choose a
stranded conductor because a solid conductor construction will break
with continuous flexing.
Coaxial cable is also
available with a copper-covered steel center conductor. The steel core
of a copper covered steel center conductor provides extra cable
strength, while its copper coating provides a path for RF signal. This
construction technique is used due to the fact that the higher the
frequency of an electronic signal transmission, the more the signal
travels on the outer surface of a conductor. This phenomena is known
as "skin effect".
A copper-covered steel
center conductor has a much higher D.C. resistance than bare copper
and greatly attenuates the lower frequency components of a CCTV video
signal (refer to table). Although it may be less expensive than pure
copper, it is not suitable for CCTV and is not recommended. Coaxial
cable that utilizes a copper-covered steel center conductor is usually
designed for, and more suitable for use in CATV and other RF
applications because the skin effect transmission characteristic at
higher frequencies.
The
attenuation chart clearly shows the difference between copper and
copper covered steel. Especially take note of the lower frequency
range where the sync pulse information is transmitted.
Notice
the big difference in attenuation between the two materials. If a
cable is chosen with copper covered steel the sync pulse information
will be attenuated causing distortion in the video signal. Another
guide-line used in the selection of center conductor construction is
the cable’s installation as to fixed or pan and tilt applications.
If the cable is going to be used on a CCTV camera that will be in a
fixed position, then a solid conductor is acceptable. However, if the
cable will be used in a pan and tilt application, then you should
choose a stranded conductor because a solid conductor construction
will eventually break under the constant strain being placed on the
cable at the same point.
Dielectric
Material
Dielectric
Material of a coax cable is also another key area that should be
addressed. The dielectric material and its composition is critical as
it sets up the electrical characteristics such as capacitance,
velocity of propagation, impedance, and attenuation of the cable.
These parameters will determine signal strength and transmission
distance. It is recommended to choose a dielectric with excellent
electrical properties such as polyethylene or FEP. Such material will
give you lower capacitance and a higher velocity of propagation. This
results in a cable with low-loss characteristics and reduced
attenuation of the signal. To improve the electrical properties even
further, a foamed or cellular composition of these materials is
recommended (see chart).
Braided
Shield
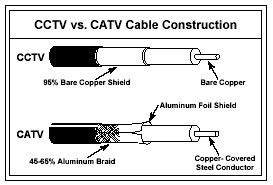
A
braided shield is the proper type of shield for CCTV and has two key
purposes. One is to provide a low D.C. resistance ground path and the
second is to provide shielding of outside interference from distorting
the video signal. The shielding should be constructed of bare copper
to provide a low D.C.R. return path. It should have a 95% or better
braid coverage in order to provide adequate shielding from outside
electrical interference’s. Anything less is usually not acceptable
for CCTV. To provide increased shielding in the RFI range, a
construction with an aluminum foil is acceptable as long as a high
percentage copper braid is used to provide the low D.C.R. return path.
|
|
A
cable with a combination aluminum foil shield and low coverage
aluminum braid (see diagram) commonly used for CATV is not acceptable!
Because aluminum shields have a much higher D.C. resistance return
path and the braided portion of these type of cables provide only a
low percentage of coverage, they do not provide the type of shielding
required for CCTV video transmission.
Jacket
Jacket
choice is mainly determined by the environment where the cable will be
installed. The cable jacket provides two major functions. One is to
provide protection from the elements a cable may be subjected to and
the second is to provide solid termination. PVC is a good choice for
most applications located inside a building. Plenum rated cables are
required for use in ducts, plenums and other space used for
environmental air without conduit as per NEC or CEC. Polyethylene is
recommended for outdoor applications where the cable may be subjected
to the elements and a high degree of moisture, sunlight, and abrasion
resistance is required. Do not install indoor rated cable in aerial,
direct burial or underground pipe. An indoor-rated cable is not
designed for these harsh environments and the electrical and
mechanical characteristics will degrade over a period of time and will
need to be replaced. Always follow the applicable code for the proper
cable type for your installation.
Coaxial
Cable Parameters
Coaxial
Cable Parameters vary depending on the type of cable construction. All
coaxial cables have a characteristic impedance. The impedance of CCTV
equipment is 75 ohms; therefore in order to have minimum losses, it is
important to choose a cable with a matching impedance of 75 ohms. If a
cable of another impedance (50 ohm or 93 ohm) is chosen, then you will
experience signal loss and reflection resulting in short distance
transmission and poor picture quality. Coaxial cables are also
available in different RG types. RG stands for Radio Guide and is a
term used when sending Radio Frequency (RF) signals down a coaxial
cable. 75 ohm coaxial cable comes in several sizes with the most
common types being RG59, RG6, and RG11. An RG59 cable is the most
commonly used because it is smaller in diameter and easy to work with.
The RG11 cable is the largest in diameter and harder to work with. The
RG6 size is between the two. The difference between the RG types is
not just size, but also the attenuation characteristics and therefore
the transmission distance. Typically, the cable transmission
limitations for CCTV will be as follows:
The
RG59 has the highest attenuation of the three types and you can expect
to get a distance of about 750 ft. (225m) - 1,000 ft. (305m)
The
RG6 has lower attenuation characteristics than RG59 and you can expect
distances of about 1,000 ft. (305m) - 1,500 ft. (457m)
The
RG11 type has the lowest attenuation characteristics and you can
expect distances of up to 2,000 ft. (610m)
These
distances are based on the fact that all cable parameters described
earlier are adhered to. If you need to go beyond 2,000 ft.(610m) then
you need to use amplifiers or use Fiber Optic cable as a method of
transmission.
Installation
Considerations
Indoor
environments are the most common for coaxial cable installations. A
few tips for installing coaxial cable are as follows:
First
and foremost, follow all NEC or CEC requirements when installing
coaxial cables.
Distribute
the pulling tension evenly over the cable and do not exceed the
minimum bend radius. Exceeding the maximum pulling tension or the
minimum bend radius of a cable can cause permanent damage both
mechanically and electrically to the cable.
When
pulling cable through conduit, clean and de-burr the conduit
completely and use proper lubricants in long runs. Outdoor
installations require special installation techniques that will enable
the cable to withstand harsh environments. When using cable in an
aerial application, lash the cable to a steel messenger wire. This
will help support the cable and reduce the stress on the cable during
wind, snow and ice storms. When direct burying a cable, lay the cable
without tension so it will not be stressed by when earth is packed
around it. When burying in rocky soil, fill the trench with sand. Lay
the cable and then place pressure-treated wood or metal plates over
the cable. This will prevent damage to the cable from rocky soil
settling. In climate areas, bury the cable below the frost line.
Termination
Techniques
The
solder method offers several advantages for connectorization. This
type of connector can be used on solid or standard conductors. It
allows for both solid mechanical and electrical connections. The
disadvantage is that it takes more time to terminate than other
methods and "cold" solder joints can cause problems if the
connector is not soldered to the cable properly.
The
Crimp Method is probably the most popular method for terminating BNC
connectors on coax cable. Like the solder method, it can be used on
solid or stranded conductors and provides a good mechanical and
electrical connection. This method is the most popular way to
terminate because there is no need for soldering; therefore
installation time is reduced. Some important points to remember when
using the crimp method is to use the proper size connector for the
size coax you are using. A tight fit on the cable is important When
crimping the connector, use the proper tool! Don’t use pliers!
Pliers are not designed to place the pressure of the crimp evenly
around the connector. Pliers will only crush the cable and can degrade
the electrical properties of the cable.
The
twist-on method is the quickest way of terminating a coaxial cable;
however, it does have some drawbacks. When terminating the cable with
this type of connector, the center conductor is cut into by the center
pin on the connector, thus to much twisting can cause damage to the
center conductor. In pan and tilt installations the constant movement
of the cable may work the connector loose and it is not recommended
for this application. Because there is no mechanical or electrical
crimp or solder connection, this connector is not as reliable as the
other methods.
Conclusion
Designing
a CCTV system takes quality components, engineering, and installation
practices. Remember the coax cable specified for a CCTV system is a
key component of the system and is critical to the proper operation of
the system. Do not install anything less than cable specifications
suitable for CCTV. By following the parameters covered in this
technical paper, you should have much success with your CCTV cabling.

![]()
